Fundamental of GC-MS
What is GC-MS ?
GC + MS = GC-MS
(Separation ) ( Identification ) (Separation Identification )
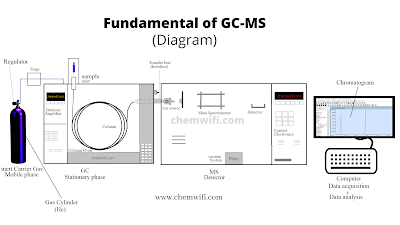
Instrumentation of GC-MS
Overview of the major hardware components of the mass Spectrometer.
- GC inlet
- Interface
- Ion source
- Mass Analyzer
- Detector
- Vacuum System
1. GC intel
The GC inlet should the three purpose.
- Place of entry
- Vaporization of sample
- Transports the sample to the column
2. Interface
Interfacing GC and MS
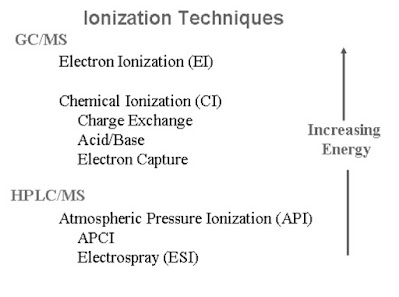
3. Ion Source
Technique by which the sample molecule is getting ionize.
The ion source serves two main purposes :
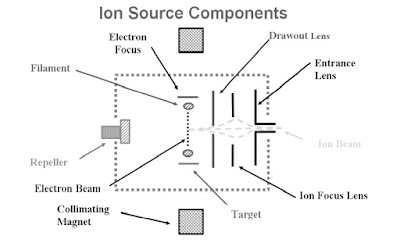
Ionization Chamber
The parts of the ionization chamber work together to provide opportunities for the molecules and
electrons to interact.
electrons to interact.
- Filament
- Magnets
- Target
- Electron Focus
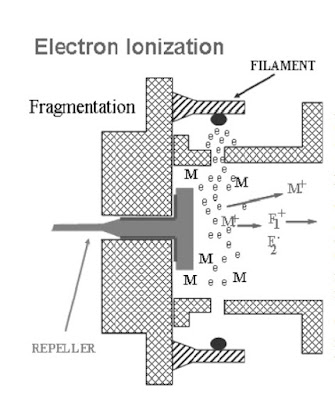
Sample molecules interact with electrons in the ionization chamber. Collisions occur, resulting
in the ionization process.
in the ionization process.
- Electron Bombardment
- Energized Molecules
- Fragmentation
- Repeated Process
As a result of the collision with the
electron, the sample molecule loses an
electron. The resulting species is called a
molecular ion. The molecular ion has a
positive charge.
M + e → M + + 2e –
The greater the electron energy, the more extensive the molecular fragmentation.
Chemical Ionization
A reagent gas is ionized by the electrons
The ionized reagent gas interacts or Colloids with the sample molecule to form ions from the sample molecule.
In Cl, ionized reagent gas molecules (G) colloids with volatile Analyte neutral molecules (M) to produce analyte ions.
Pseudo-molecular ion MH+ ( Positive ion mode) or [M-H]– ( Negative ion mode) are often observed.
Positive ion mode: GH+ + M → MH+ + G
Negative ion mode:[G-H]– + M → [M-H]– + G
Positive Chemical Ionization (PCI)
- First form ions from a “reagent gas ” by bombardment with electrons.
- Reagent gas ions under go subsequent reactions with sample molecules to form sample ions (“Bronsted acid”).
- Cl ion information is much more “gentle” than electron ionization (EI) three fore less fragmentation.
- most common reagent gas is methane, produces ions with almost any sample molecule.
- Other reagent gases (isobutane, ammonia) are more selective and even less fragmentation.
- Source pressure – 0.2 Torr
- Detection limits are generally high because of background from the reagent gas (methane)
- most often used to determine the molecular weight of a compound.
Negative Chemical Ionization (NCI)
- a.k.a “electron capture negative ion chemical ionization “.
- First form a “Cloud” of electrons with little excess energy (“thermal electrons”)
- “Thermal electrons” are captured by sample molecules
- Buffer gas required (removes energy from electrons/ions)
- Methane is by far the most often used buffer gas.
- Source pressure – 0.4 torr ( higher than for PCI mode)
- only certain types of molecules are capable of capturing thermal electrons (selectivity)
- Extremely efficient for some molecules (selectivity).
- Detection limits are generally very low due to lack of response from contaminants or matrix.
- most often used for selective high sensitivity analysis.
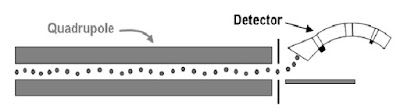
4. Mass Analyzer
Mass Filters – Quadrupole
Ionized molecule from the ion source are directed to the Quadrupole.
The Quadrupole filter the ion according the m/z ( mass-to-charge) ratio.
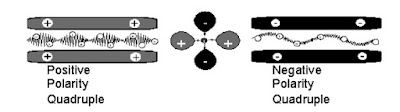
The traditional quadrupole consists of 4 independent rods mode
A Quadrupole can be monolithic. The four hyperbolic surf are made using a single of quartz. The inner sur conductive.
Quadrupole – Function
The 4 quadrupole rods have an electrical jumper between
each pair of rods. Electrically, the pairs of rods have
opposite potentials. Although the rod pairs have opposite
charges, the four rods work together to move the ions of
selected mass through the quadrupole.
each pair of rods. Electrically, the pairs of rods have
opposite potentials. Although the rod pairs have opposite
charges, the four rods work together to move the ions of
selected mass through the quadrupole.
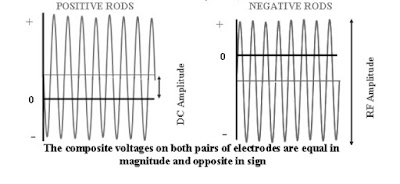
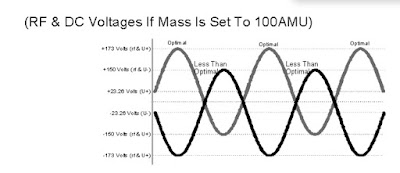
With the correct amount of RF and DC applied to the quadrupole, an ion of a particular selected
mass will make it through the mass filter. The higher the RF and DC amplitude, the higher the
mass selected. The lower the RF and DC amplitudes, the lower the mass selected.
mass will make it through the mass filter. The higher the RF and DC amplitude, the higher the
mass selected. The lower the RF and DC amplitudes, the lower the mass selected.
5. Detectors
Ionized sample has been separated by mass to- charge ratio in the quadrupole the abundance of each ion must be detected and reported to the data system. This involves and ion detector an electron multiplier and a high gain amplifier.
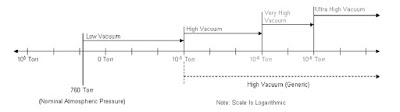
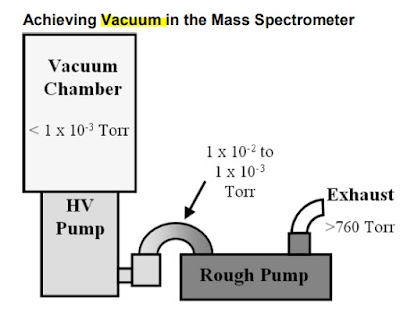
6. Vacuum System
Reasons for Vacuum in MS.
Pressure Mean Free path
(Torr) (Meters)
760 6 * 10-8
1 4.5 * 10-5
10-3 4.5 * 10-2
10-5 4.5 * 10
10-7 4.5 * 102
10-9 4.5 * 104
- Provide adequate mean free path
- Provide collision-free ion trajectories
- Reduce ion-molecular reactions
- Reduce background interference
- increase filament life time.
- Avoid electrical discharge
- increase sensitivity
-
Read More….


Hi! Quick question that’s entirely off topic. Do you know how to
make your site mobile friendly? My weblog looks weird when viewing from my iphone4.
I’m trying to find a thwme or plugin that might be able to resolve this problem.
If you have any suggestions, please share.
Thanks!