Fiber Analysis: Qualitative

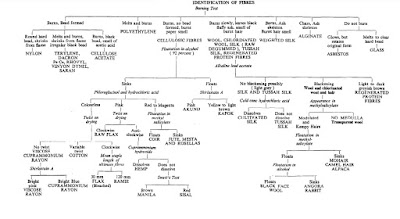
1. Grouped By Generic Classifications of Textile Fibres
Group 1 – Natural Fibers
|
Natural Fibers
|
|
|
a.
Cellulose (Vegetable)
|
b.
Keratin (Animal)
(Natural
Protein Fibres)
|
c.
Mineral
|
|
|
1.
Seed Fibres
Cotton
Akund
Kapok
|
1.
Wool & Chlorinated wool
|
·
Asbestos
|
|
|
2.
Silk
Bombyx
(cultivated)
Tasar
or Tussah (wild)
|
|
|
2.
Bast Fibres
I. Low Lignin Content
Linen or Flax
Ramie
II. High Lignin Content
Jute
Mesta
Rosella
True Hemp
Sunn Hemp
|
|
|
3.
Alpaca
Camel
Cashmere
Horse
llama
Mohair
Rabbit
Vicuna
Yak
|
|
|
3.
Leaf Fibres
Manila
Hemp (Abaca)
Sisal
(Agave)
|
|
|
4.
Fruit or Nut Fibre
Coir
|
|
Group 2 – Man-Made Fibers
|
Man Made Fibers
|
|
|
a.
Regenerated Fibres
|
b.
Synthetic Fibres
|
|
|
1.
Cellulosic
Viscose
Cuprammonium
Acetate
(secondary & triacetate)
Polynosic
High-Wet
Modulus Fibres (HWM)
|
1.
Polyamides
Nylon
6
Nylon
66
Nylon
610
Etc…
|
|
|
2.
Polyester
Terylene
Terene
Dacron
Etc…
|
|
|
2.
Protein
Casein
Groundnut
Fibre
Zein
|
|
|
3.
Polyvinyl Derivatives
I.
Polyvinyl
Chloride
Pe Ce
Rhovyl
Etc…
II.
Polyvinyl
Chloride Acetate
Vinylon
ST
Vinyon
HH
III.
Polyvinyl Chloride Acrylonitrile
Vinyon
N
Dynel
IV.
Polyvinylonitrile (Acrylic fibre)
Orlon
Acrilan
V.
Polyvinyl
Alcohol
Vinylon
Kuralon
VI.
Polystyrene
& Copolymers
Styroflex
Polyfil
Etc..
VII.
Polyvinylidene Chloride & Copolymers
Saran
Velon
|
|
|
4.
Polyolefins
I.
Polyethylene
Polythene
II.
Polypropylene
Reevon
|
|
Group 3 – Inorganic Fibers
Inorganic Fibres
a. Glass
b. Metal
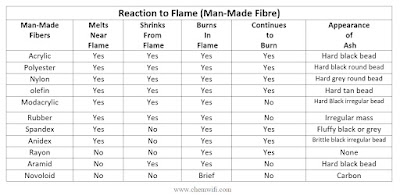
2. Fibre identification by Burning Test-
A small tuft of fibres is held by forceps in the frame of a micro-burner for about
10 seconds and is then removed. It is noted whether the tuft burns or not; whether it forms any bead or whether the ash skeleton is retained; the type of smell emitted during burning is also noted. The test is carried out in daylight.
Reaction to Flame
3. Fibre identification by Density
Identification Density & Melting
Point
|
Natural Fibre
|
Density g/cc
|
Melting Point ℃
|
Asbestos (chrysotile)
|
2.1-2.8
|
Over 350
|
Cellulose
|
1.51
|
none
|
Silk
|
1.32-1.34
|
none
|
Wool & Other Hair
|
1.15-1.30
|
none
|
Identification Density & Melting
Point
|
Man-Made Fibre
|
Density g/cc
|
Melting Point ℃
|
Acetate, Secondary
|
1.32
|
260
|
Acetate, tri
|
1.30
|
288
|
Acrylic
|
1.12-1.19
|
none
|
Anidex
|
1.22
|
Softens at 190℃
|
Aramid
|
1.38
|
Char at 400℃
|
Azlon
|
1.30
|
none
|
Modacrylic
|
1.30 or 1.36
|
188 or 120
|
Novoloid
|
1.25
|
none
|
Nylon
|
1.12-1.15
|
213-225
|
Nylon 6,6
|
1.12-1.15
|
256-265
|
Nytril
|
1.20
|
218
|
Polyester
|
1.38 or 1.23
|
250-260 or 282
|
Polyethylene
|
0.90-0.92
|
135
|
polypropylene
|
0.90-0.92
|
170
|
Rayon
|
1.51
|
none
|
Rubber
|
0.96-1.06
|
none
|
Saran
|
1.70
|
168
|
Spandex
|
1.20-1.21
|
230
|
Vinal
|
1.26-1.30
|
–
|
Vinyon
|
1.34-1.37
|
230 or 400
|
Identification Density & Melting
Point
|
Inorganic Fibre
|
Density g/cc
|
Melting Point ℃
|
Metallic
|
Varies
|
Over 300
|
Glass
|
2.4-2.6
|
850
|
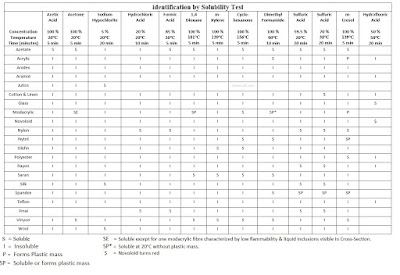
4. Fibre identification by Solubility Test
Floatation Test –
A small sample of the fibre after degreasing in benzene-methanol mixture ( 3:2 ) is placed in the test liquid and pushed below the surface by means of a glass rod. The liquid should be illuminated transversely and viewed against a black background to observe whether the sample floats on the surface or sinks.
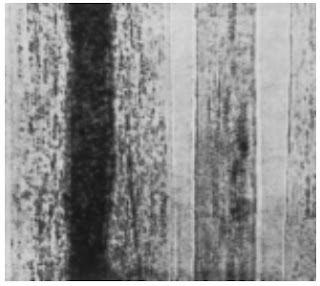
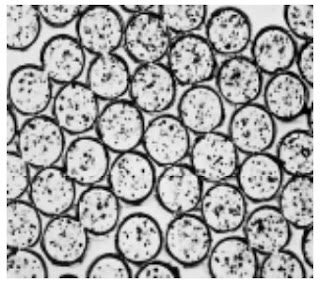
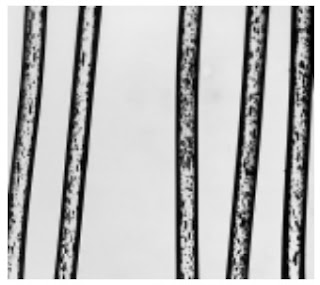
5. Fibre identification by Microscope
Microscopic Analysis
Longitudinal Examination – Place a small number of fibres on a glass slide in a suitable
mounting medium, cover the fibres with a covering glass. Examine the fibres at a specified magnification under microscope.
Cross-Section Examination – Take a tuft of fibres and prepare the specimen with the
cross-sectioning device, place it on a glass slide in a suitable mounting medium and cover it with a covering glass. Examine the fibres at a specified magnification under microscope.
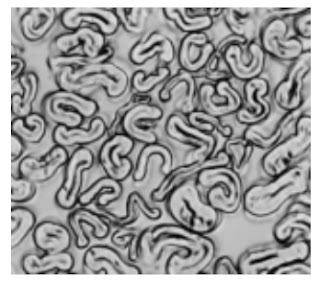
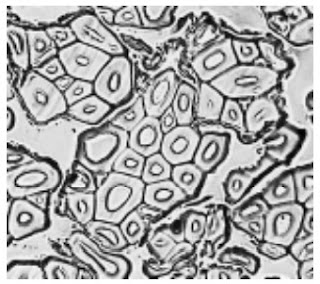
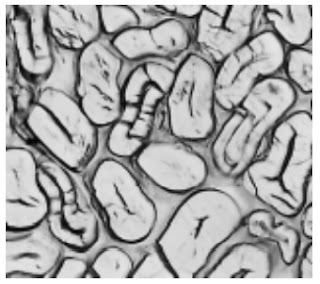
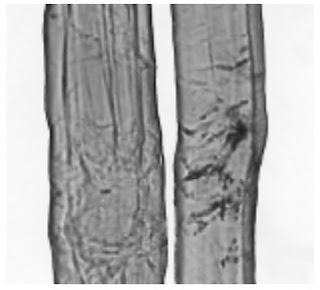
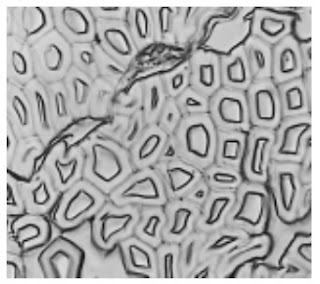
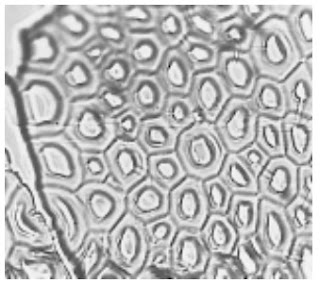
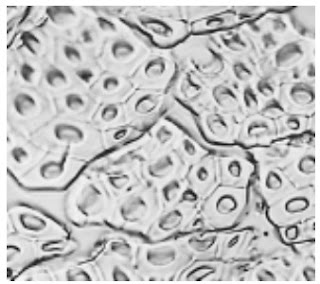
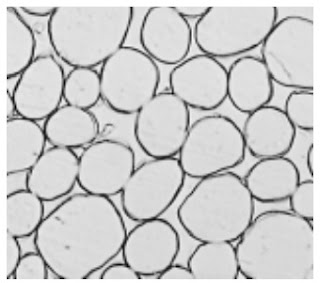
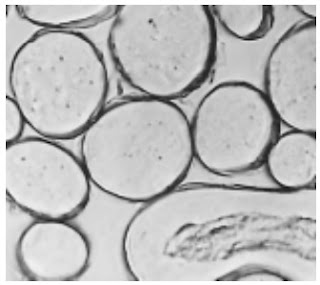
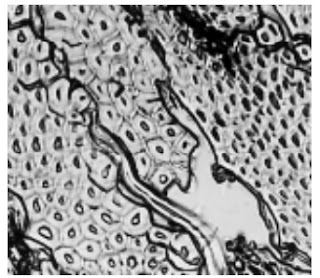
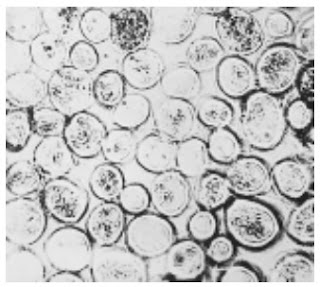
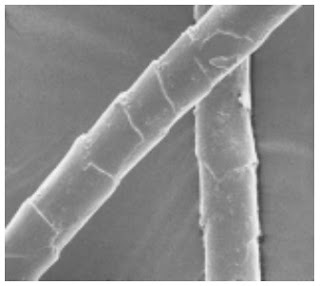
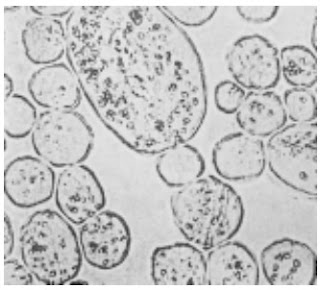
Photomicrographs of Common Textile Fibers
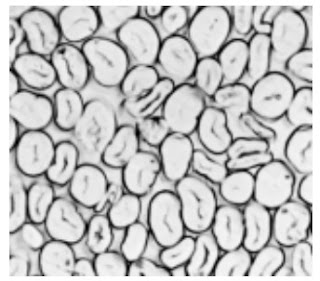
Cross-Section 500X – Cotton fibre (not mercerized)
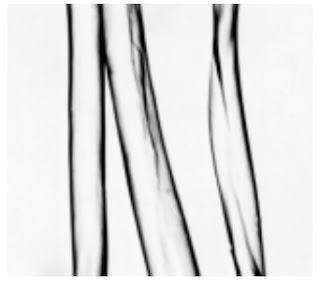
Longitudinal View-500X – Cotton fibre (not mercerized)
Cross-Section 500X – Cotton fibre (mercerized)
Longitudinal View-500X – Cotton fibre (mercerized)
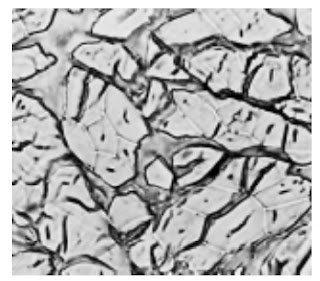
Cross-Section-500X Flax fibre
Longitudinal-View-500X-Flax fibre
Cross-Section-500X- Hemp fibre
Longitudinal-View-500X-Hemp fibre
Cross-Section-500X- Jute fibre
Longitudinal-View-500X-jute-fibre
Cross-Section-500X-Ramie fibre
Longitudinal-View-500X-Ramie fibre
Cross-Section-500X- Sisal fibre
Longitudinal-View-500X-Sisal fibre
Cross-Section-500X-Abaca fibre
Longitudinal-View-500X-Abaca fibre
Cross-Section-500X-Kenaf-fibre
Longitudinal-View-500X-Kenaf-fibre
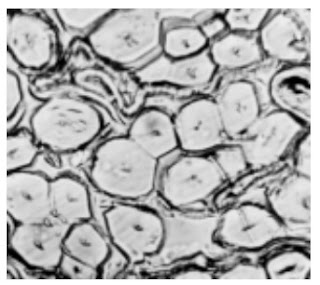
Cross-Section-500X-Wool-fibre
Longitudinal-View-500X-Wool fibre
Cross-Section-500X-Mohair fibre
Longitudinal-View-500X-Mohair-fibre
Cross-Section-500X-Phormium-fibre
Longitudinal-View-500X- Phormium fibre
Cross-Section-500X- Cashmere fibre
Longitudinal-View-240X- Cashmere fibre
Longitudinal-View-1500X- Cashmere fibre
Cross-Section-500X-Camel hair
Longitudinal-View-500X-Camel-hair-fibre
Cross-Section-500X-Silk-fibre
Longitudinal-View-500X-silk-fibre
Cross-Section-500X-Silk-tussah-fibre
Longitudinal-View-500X-silk-tussah-fibre
Cross-Section-500X- Polyester fibre
Longitudinal-View-250X-Polyester-fibre
REFFERENCE SPECIFICATION : IS 667: 1981 & AATCC 20- 2007